

10.18 ‘Network error: Connection timed out’.10.17 ‘Network error: Connection refused’.10.16 ‘Network error: Connection reset by peer’.
Putty ssh auth software#
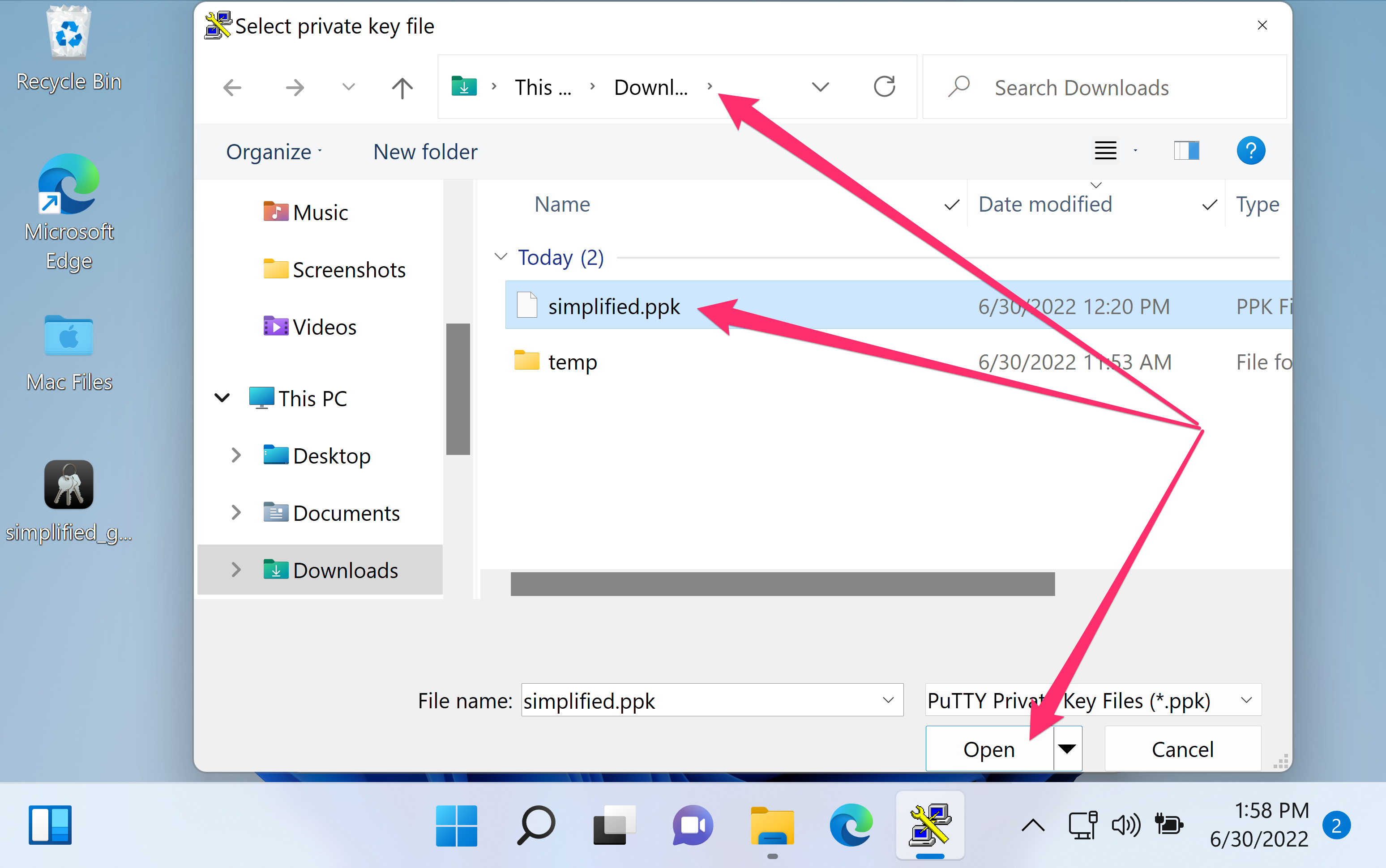
10.13 ‘Incoming packet was garbled on decryption’.10.12 ‘Incorrect MAC received on packet’ or ‘Incorrect CRC received on packet’.10.11 ‘No supported authentication methods available’.10.10 ‘Access denied’, ‘Authentication refused’.10.9 ‘Server refused our key’, ‘Server refused our public key’, ‘Key refused’.10.8 ‘Unable to use key file’, ‘Couldn't load private key’, ‘Couldn't load this key’.10.7 ‘Internal error’, ‘Internal fault’, ‘Assertion failed’.10.5 ‘Remote side sent disconnect message type 2 (protocol error): "Too many authentication failures for root"’.10.4 ‘The first cipher supported by the server is.10.3 ‘SSH protocol version 2 required by our configuration but remote only provides (old, insecure) SSH-1’.10.2 ‘WARNING - POTENTIAL SECURITY BREACH!’.10.1 ‘The server's host key is not cached in the registry’.9.5 Loading keys without decrypting them.Chapter 9: Using Pageant for authentication.8.3 Getting ready for public key authentication.
Putty ssh auth generator#
8.2 Using PuTTYgen, the PuTTY key generator.8.1 Public key authentication - an introduction.Chapter 8: Using public keys for SSH authentication.7.3 Using Plink in batch files and scripts.Chapter 7: Using the command-line connection tool Plink.6.3 Using public key authentication with PSFTP.Chapter 6: Using PSFTP to transfer files securely.Chapter 5: Using PSCP to transfer files securely.4.27 The ‘Bare ssh-connection’ protocol.3.10 Connecting using the SUPDUP protocol.3.9 Connecting using the Rlogin protocol.3.8 Connecting using the Telnet protocol.3.3 Altering your character set configuration.3.2 Creating a log file of your session.1.2 How do SSH, Telnet, Rlogin, and SUPDUP differ?.1.1 What are SSH, Telnet, Rlogin, and SUPDUP?.See appendix D for the licence text in full.
You may distribute this documentation under the MIT licence.
Putty ssh auth manual#
This manual is copyright 1997-2021 Simon Tatham. The only Unix-specific documentation that currently exists is the man pages. Some options are therefore mentioned that are absent from the Unix version the Unix version has features not described here and the pterm and command-line puttygen and pageant utilities are not described at all. Note to Unix users: this manual currently primarily documents the Windows versions of the PuTTY utilities. This manual documents PuTTY, and its companion utilities PSCP, PSFTP, Plink, Pageant and PuTTYgen. PuTTY is a free (MIT-licensed) Windows Telnet and SSH client. You can download Bitvise SSH Server here.Previous | Contents | Index | Next PuTTY User Manual The SSH Server is developed and supported professionally by Bitvise. It is robust, easy to install, easy to use, and works well with a variety of SSH clients, including Bitvise SSH Client, OpenSSH, and PuTTY. You can download it here.īitvise SSH Server is an SSH, SFTP and SCP server for Windows.
Putty ssh auth code#
PuTTY is open source software that is available with source code and is developed and supported by a group of volunteers.īelow suggestions are independent of the authors of PuTTY. PuTTY is an SSH and telnet client, developed originally by Simon Tatham for the Windows platform. Download PuTTY - a free SSH and telnet client for Windows


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
